Product Description
Product Description
| Material | Aluminium Alloy,Carbon Steel,Stainless steel,Copper,Brass,Nylon,Plastic(Customized Material) |
| Producing Equipment | 3 Axis,4 Axis,5 Axis CNC Machines,Automatic Lathe Machines,Stamping Machines,CNC Milling machines,CNC Turning Machines,Turning Milling Compound Machines,Grinding Machines,Rolling Machines,Laser Machines. |
| Surface Treatment | Anodizing,Polishing,Electroplating,Heat Treatment,Spray Paint,Sand Blasting. |
| Testing Equipment | Salt Spray Test, Hardness Tester, Coating Thickness Tester, Two Dimensions Measuring Instrument. |
| Quality Testing | 100% Quality Inspection Before Shipment. |
| Lead Time | Generally, The Delivery Date Is 7-15 Days,Delivery Time of Bulk Order Is More Than 15 days. |
| Tolerance and Roughness | Size Tolerance:+/-0.005 – 0.01mm,Roughness: Ra0.2 – Ra3.2 (Custom Size Requirements) |
| Cargo Shipment | Express(DHL,Fedex,UPS, TNT ),Air shipment+Local Express Delivery,Ocean Shipment. |
| Main Markets | America, Europe, Australia, Asia. |
| Payment Type | T/T, L/C, Paypal,Western Union,Others. |
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
HangZhou Fuyouda Technology Co., Ltd. Was established in city known as the “world factory”-HangZhou. We are factory and have many kinds of machine, such as 5-axis CNC machines, lath machines, turning milling compound machines. After 10 years of R&D, production and sales, we have 80% market share in the field of 3D printer parts in China and we are specializing in CNC machinig for 10 years. We are committed to creating a work and production environment that is above the industry average. We adopt scientific production management methods to improve production efficiency and reduce production costs. Please believe and choose us! We adhere to the management principles of “Quality First, Customer first and Credit-based” since the establishment of the company and always do our best to satisfy potential needs of our customers. Our company is sincerely willing to cooperate with enterprises from all over the world in order to realize a CHINAMFG situation since the trend of economic globalization has developed with anirresistible force.
Our Advantages
FAQ
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Color: | Customized |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Standard: | International |
| Type: | Connection |
| Material: | Cast Iron |
| Samples: |
US$ 3.8/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What lubrication and maintenance practices are required for spiral gears?
Spiral gears require proper lubrication and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here are the recommended lubrication and maintenance practices for spiral gears:
- Lubrication: Adequate lubrication is essential for smooth gear operation and to minimize wear. The lubricant forms a protective film between the gear teeth, reducing friction and preventing metal-to-metal contact. It is crucial to use a lubricant that is compatible with the gear material, operating conditions, and load requirements. Regular lubrication intervals should be followed, and the lubricant should be replenished as needed.
- Lubricant Selection: The selection of the lubricant depends on various factors such as gear speed, load, temperature, and environment. It is recommended to consult the gear manufacturer or lubrication experts to determine the most suitable lubricant for the specific application. The lubricant should have appropriate viscosity, additives, and temperature resistance to provide effective lubrication and protect against wear and corrosion.
- Lubricant Application: The lubricant should be applied evenly to the gear teeth and mating surfaces. Depending on the gear design and accessibility, lubrication can be done through oil bath immersion, oil splash, forced circulation, or grease application. It is important to follow the gear manufacturer’s guidelines or industry best practices for proper lubricant application.
- Monitoring and Inspection: Regular monitoring and inspection of the gear condition are essential for early detection of any abnormalities or signs of wear. This can include visual inspections, checking for unusual noise or vibrations, and measuring gear backlash and tooth wear. Monitoring can help identify potential issues and allow for timely maintenance or lubricant adjustments before significant damage occurs.
- Cleaning and Contaminant Control: Regular cleaning of the gears and their surrounding areas is necessary to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can affect gear performance and lubrication. Contaminants can accelerate wear and cause damage to the gear teeth. Proper sealing and contamination control measures should be implemented to minimize the ingress of contaminants into the gear system.
- Maintenance Schedule: Establishing a maintenance schedule is important to ensure timely lubricant replenishment, gear inspections, and necessary repairs or replacements. The maintenance schedule should consider the operating conditions, gear load, and manufacturer’s recommendations. Adhering to a well-planned maintenance schedule helps prolong the service life of spiral gears and ensures their continued performance.
By following these lubrication and maintenance practices, spiral gears can maintain their efficiency, durability, and reliability over time. Regular attention to lubrication, monitoring, and maintenance contributes to the smooth operation and extended lifespan of spiral gears in various applications.

How do you calculate the gear ratio in a spiral gear system?
The gear ratio in a spiral gear system can be calculated by comparing the number of teeth on the driving gear (pinion) to the number of teeth on the driven gear (gear). The gear ratio represents the ratio of the angular velocity (speed) of the driving gear to the angular velocity of the driven gear. Here’s the formula to calculate the gear ratio:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Driven Gear / Number of Teeth on Driving Gear
For example, consider a spiral gear system where the driving gear (pinion) has 20 teeth, and the driven gear (gear) has 40 teeth. The gear ratio can be calculated as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 / 20 = 2
In this example, the gear ratio is 2, which means the driven gear will rotate at half the speed of the driving gear. This calculation assumes that the gears have the same module (gear size) and that there are no additional gear stages in the system.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio determines the speed and torque relationship between the driving and driven gears. A gear ratio greater than 1 (e.g., 2, 3, etc.) indicates a reduction in speed and an increase in torque, while a gear ratio less than 1 (e.g., 0.5, 0.75, etc.) indicates an increase in speed and a reduction in torque.
When working with spiral gears, it’s essential to consider the helix angle and axial thrust in addition to the gear ratio to ensure proper gear design and performance.
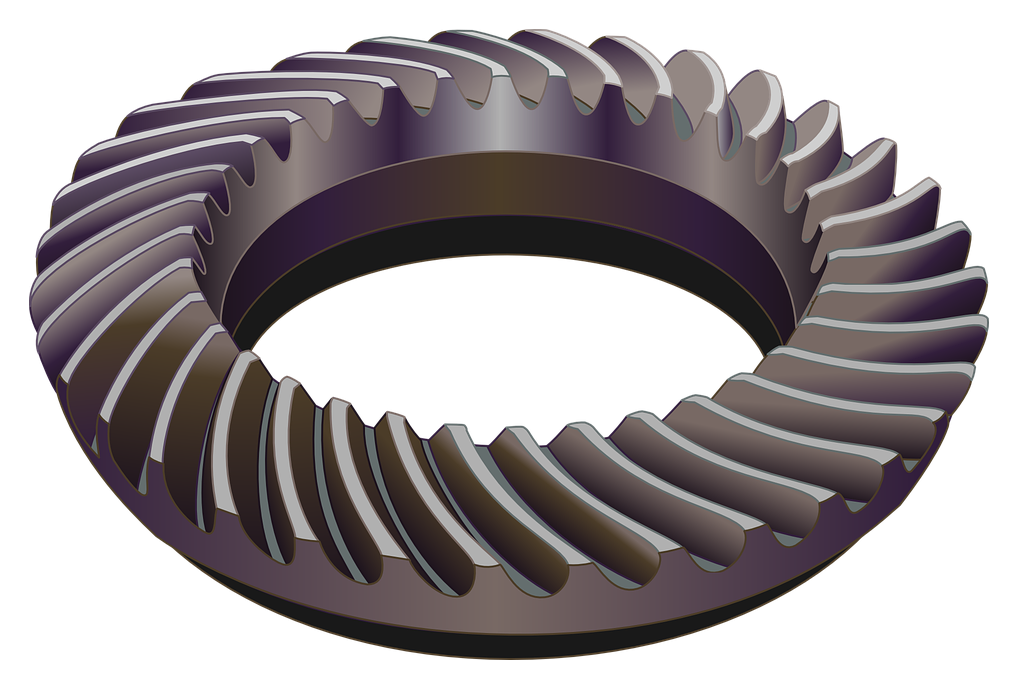
How do spiral gears differ from other types of gears?
Spiral gears, also known as helical gears, have distinct differences compared to other types of gears. These differences primarily stem from the helical tooth arrangement in spiral gears. Here’s how spiral gears differ from other gear types:
- Helical Tooth Arrangement: Spiral gears have teeth that are curved in a spiral pattern, forming a helix. This is different from straight-cut gears, which have teeth parallel to the gear axis, or bevel gears, which have teeth on conical surfaces. The helical tooth arrangement in spiral gears provides various advantages such as smoother operation, increased load capacity, and improved efficiency.
- Gradual Tooth Engagement: Due to the helical tooth arrangement, spiral gears have a gradual tooth engagement as the gears rotate. This gradual contact reduces impact and noise during gear meshing, resulting in smoother and quieter operation compared to straight-cut gears.
- Axial Thrust Compensation: Spiral gears can be designed with opposite helix angles on mating gears, which helps in canceling out the axial thrust generated during gear meshing. This feature eliminates the need for additional thrust bearings and simplifies the gear design, reducing complexity.
- Load Distribution: The helical tooth arrangement in spiral gears allows the load to be distributed over multiple teeth. This enables spiral gears to handle higher torque transmission and carry heavier loads compared to straight-cut gears.
- Efficiency: Spiral gears exhibit higher efficiency due to reduced sliding friction between the teeth. The helical tooth arrangement helps minimize sliding friction, resulting in lower power losses during gear operation.
- Versatility: Spiral gears can be manufactured in various configurations, including spur, helical, and double helical designs. This versatility allows for their application in a wide range of machinery and systems, providing flexibility in gear design and usage.
These differences make spiral gears well-suited for applications that require smooth operation, high load capacity, and efficient power transmission. They are commonly used in gearboxes, automotive differentials, machine tools, and various industrial machinery.
In summary, spiral gears stand out from other gear types due to their helical tooth arrangement, resulting in smoother operation, increased load capacity, improved efficiency, and versatility.


editor by CX 2024-01-04